大厂如何用一道编程题考察候选人水平
来源:https://juejin.cn/post/6987529814324281380
作者:高晓晨
进入正题
面试环节对面试官的一些挑战
- 面试官和候选人的知识结构可能有差异 => 可能会错过优秀的人
- 遇到「面霸」,频繁面试刷题,但是实际能力一般 => 招到不合适的人
- 要在短短半个小时到一个小时内判断一个人,其实很难
相对靠谱的做法
- 笔试:"Talk is cheap, show me the code"
笔试常见的问题
- 考通用算法,Google 能直接搜到,失去考察意义
- 题目难度设计有问题。要么满分,要么零分,可能错过还不错的同学
- 和实际工作内容脱节
我认为好的笔试题
- 上手门槛低,所有人多多少少都能写一点,不至于开天窗
- 考点多,通过一道题可以基本摸清候选人的代码综合素养
- 给高端的人有足够的发挥空间。同样的结果,不同的实现方式可以看出候选人的技术深度
我常用的一道笔试题
很普通的一道题
1// 假设本地机器无法做加减乘除运算,需要通过远程请求让服务端来实现。 2// 以加法为例,现有远程API的模拟实现 3 4const addRemote = async (a, b) => new Promise(resolve => { 5 setTimeout(() => resolve(a + b), 1000) 6}); 7 8// 请实现本地的add方法,调用addRemote,能最优的实现输入数字的加法。 9async function add(...inputs) { 10 // 你的实现 11} 12 13// 请用示例验证运行结果: 14add(1, 2) 15 .then(result => { 16 console.log(result); // 3 17}); 18 19 20add(3, 5, 2) 21 .then(result => { 22 console.log(result); // 10 23}) 24
答案一 最基本的答案,如果写不出来,那大概率是通过不了了
1async function add(...args) { 2 let res = 0; 3 if (args.length <= 2) return res; 4 5 for (const item of args) { 6 res = await addRemote(res, item); 7 } 8 return res; 9}
递归版本
async function add(...args) {
let res = 0;
if (args.length === 0) return res;
if (args.length === 1) return args[0];
const a = args.pop();
const b = args.pop();
args.push(await addRemote(a, b));
return add(...args);
}
常见的问题:
- 没有判断入参个数
- 仍然用了本地加法
答案二 有候选人的答案如下:
1// Promise链式调用版本 2async function add(...args) { 3 return args.reduce((promiseChain, item) => { 4 return promiseChain.then(res => { 5 return addRemote(res, item); 6 }); 7 }, Promise.resolve(0)); 8 9}
从这个实现可以看出:
- 对 Array.prototype.reduce 的掌握
- 对于 Promise 链式调用的理解
- 考察候选人对 async function 本质的理解
这个版本至少能到 70 分
答案三 之前的答案结果都是对的,但是我们把耗时打出来,可以看到耗时和参数个数成线性关系,因为所有计算都是串行的,显然不是最优的解。
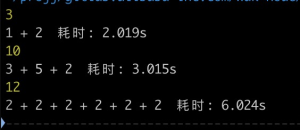
预览
更好一点的答案:
1function add(...args) { 2 if (args.length <= 1) return Promise.resolve(args[0]) 3 const promiseList = [] 4 for (let i = 0; i * 2 < args.length - 1; i++) { 5 const promise = addRemote(args[i * 2], args[i * 2 + 1]) 6 promiseList.push(promise) 7 } 8 9 if (args.length % 2) { 10 const promise = Promise.resolve(args[args.length - 1]) 11 promiseList.push(promise) 12 } 13 14 return Promise.all(promiseList).then(results => add(...results)); 15} 16

预览
可以看到很明显的优化。
答案四 还能再优化吗? 有些同学会想到加本地缓存
1const cache = {}; 2 3function addFn(a, b) { 4 const key1 = `${a}${b}`; 5 const key2 = `${b}${a}`; 6 const cacheVal = cache[key1] || cache[key2]; 7 8 if (cacheVal) return Promise.resolve(cacheVal); 9 10 return addRemote(a, b, res => { 11 cache[key1] = res; 12 cache[key2] = res; 13 return res; 14 }); 15} 16
加了缓存以后,我们再第二次执行相同参数加法时,可以不用请求远端,直接变成毫秒级返回
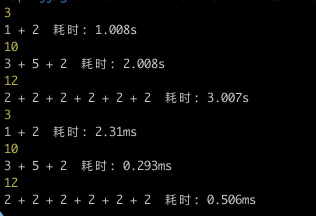
预览
其他考察点
有些时候会让候选人将代码提交到 Github 仓库,以工作中一个实际的模块标准来开发,可以考察:
- git 操作,commit 规范
- 工程化素养
- 是否有单元测试
- 覆盖率是否达标
- 依赖的模块版本如何设置
- 如何配置 ci/cd
- 文档、注释
- ...
更加开放的一种笔试形式
- 给一道题目,让候选人建一个 Github 仓库来完成
- 题目有一定难度,但是可以 Google,也可以用三方模块,和我们平时做项目差不多
- 通常面向级别较高的候选人
实际题目
// 有一个 10G 文件,每一行是一个时间戳,
// 现在要在一台 2C4G 的机器上对它进行排序,输出排序以后的文件
// 案例输入
// 1570593273487
// 1570593273486
// 1570593273488
// …
// 输出
// 1570593273486
// 1570593273487
// 1570593273488
// …
先看一个答案,看看哪里有问题
async function sort(inputFile, outputFile) {
const input = fs.createReadStream(inputFile);
const rl = readline.createInterface({ input });
const arr = [];
for await (const line of rl) {
const item = Number(line);
arr.push(item);
}
arr.sort((a, b) => a - b);
fs.writeFileSync(outputFile, arr.join('\n'));
}
10GB 的文件无法一次性放进内存里处理,内存只有 4GB
再看一个神奇的答案,只有一行代码,而且从结果来说是正确的。但不是我们笔试想要的答案。
const cp = require('child_process');
function sort(inputFile, outputFile) {
cp.exec(`sort -n ${inputFile} > ${outputFile}`);
}
解题思路
- 既然没办法一次性在内存中排序,那我们能否将 10GB 的文件拆分成若干个小文件
- 小文件先分别排序,然后再合并成一个大的文件
再将问题拆解
- 拆分大文件到小文件
- 小文件在内存里排序
- 合并所有小文件成一个整体排序过的大文件
本题最难的点在于如何合并所有小文件。代码如何实现?
- 这里需要用到一种数据结构:堆
- 堆:就是用数组实现的一个二叉树
- 堆分为:最大堆和最小堆,下面是一个最小堆(父节点小于它的子节点)
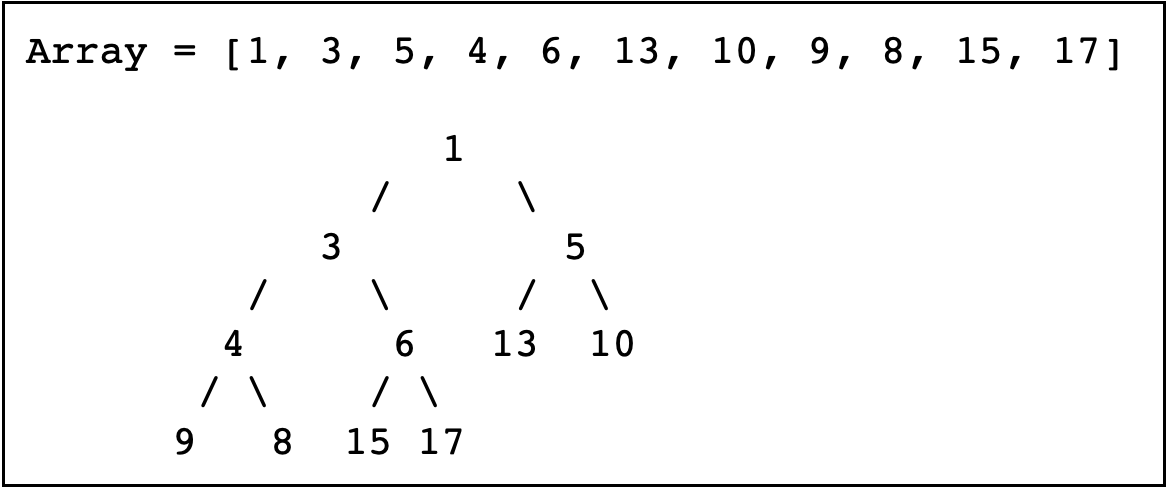
预览
堆有一些特性:
- 对于一个父节点来说
- 左节点位置:父节点位置 * 2 + 1
- 右节点位置:父节点位置 * 2 + 2
- 很容易查找最大值 / 最小值
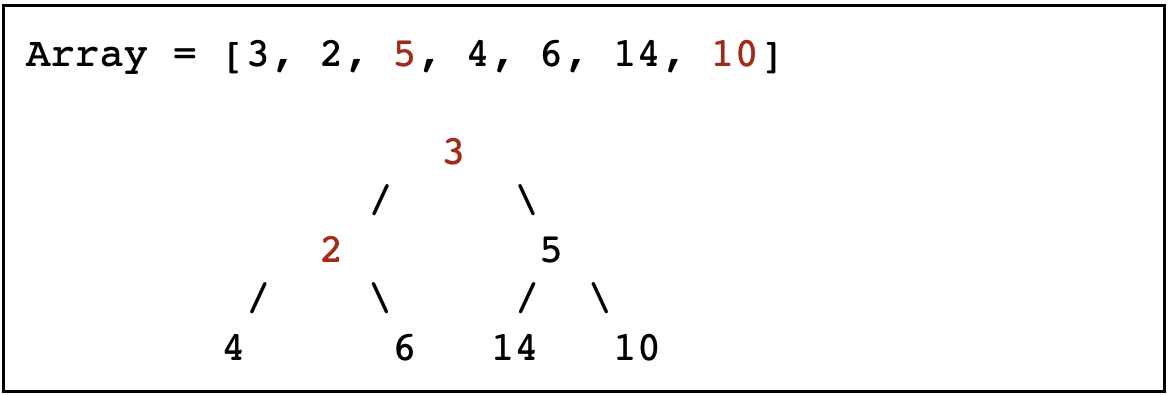
我们尝试把下面数组构造成一个最小堆
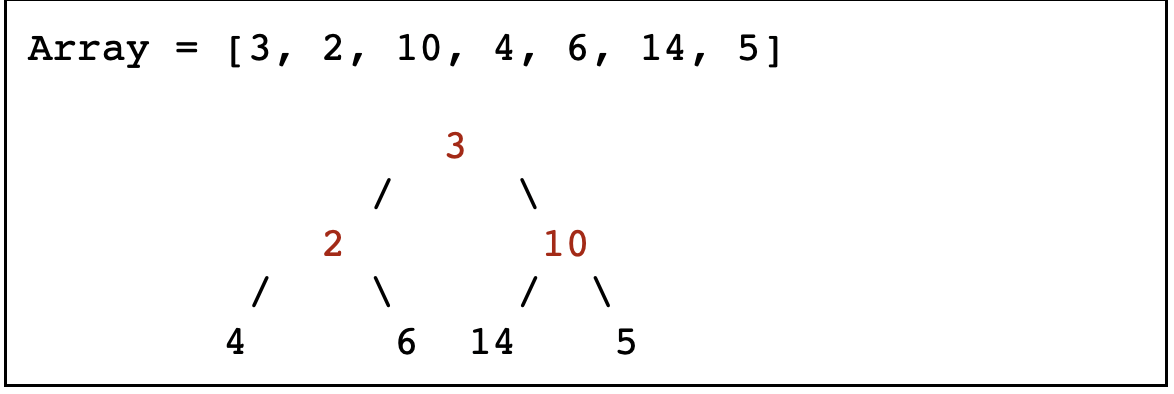
预览
-
从最后一个非叶子节点开始往前处理
-
10 比 5 大,所以交换它们的位置
 预览
预览 -
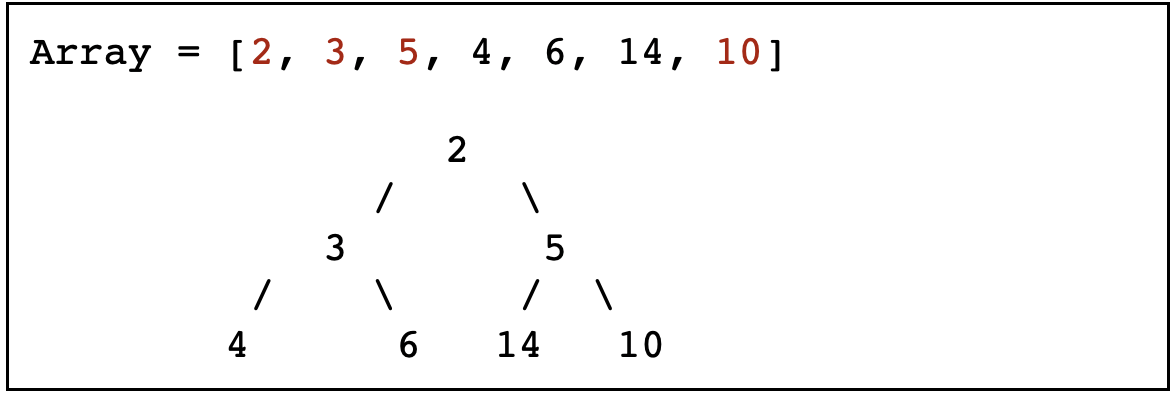
然后是节点 2,符合要求不需要处理
-
最后到顶点 3,它比左子节点大,所以要交换
 预览
预览
