问答题【61/72】说说webpack中常见的Plugin?解决了什么问题?
参考答案:
一、是什么
Plugin(Plug-in)是一种计算机应用程序,它和主应用程序互相交互,以提供特定的功能
是一种遵循一定规范的应用程序接口编写出来的程序,只能运行在程序规定的系统下,因为其需要调用原纯净系统提供的函数库或者数据
webpack中的plugin也是如此,plugin赋予其各种灵活的功能,例如打包优化、资源管理、环境变量注入等,它们会运行在 webpack 的不同阶段(钩子 / 生命周期),贯穿了webpack整个编译周期
目的在于解决loader 无法实现的其他事
配置方式
这里讲述文件的配置方式,一般情况,通过配置文件导出对象中plugins属性传入new实例对象。如下所示:
1const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin'); // 通过 npm 安装 2const webpack = require('webpack'); // 访问内置的插件 3module.exports = { 4 ... 5 plugins: [ 6 new webpack.ProgressPlugin(), 7 new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ template: './src/index.html' }), 8 ], 9};
二、特性
其本质是一个具有apply方法javascript对象
apply 方法会被 webpack compiler 调用,并且在整个编译生命周期都可以访问 compiler 对象
1const pluginName = 'ConsoleLogOnBuildWebpackPlugin'; 2 3class ConsoleLogOnBuildWebpackPlugin { 4 apply(compiler) { 5 compiler.hooks.run.tap(pluginName, (compilation) => { 6 console.log('webpack 构建过程开始!'); 7 }); 8 } 9} 10 11module.exports = ConsoleLogOnBuildWebpackPlugin;
compiler hook 的 tap 方法的第一个参数,应是驼峰式命名的插件名称
关于整个编译生命周期钩子,有如下:
- entry-option :初始化 option
- run
- compile: 真正开始的编译,在创建 compilation 对象之前
- compilation :生成好了 compilation 对象
- make 从 entry 开始递归分析依赖,准备对每个模块进行 build
- after-compile: 编译 build 过程结束
- emit :在将内存中 assets 内容写到磁盘文件夹之前
- after-emit :在将内存中 assets 内容写到磁盘文件夹之后
- done: 完成所有的编译过程
- failed: 编译失败的时候
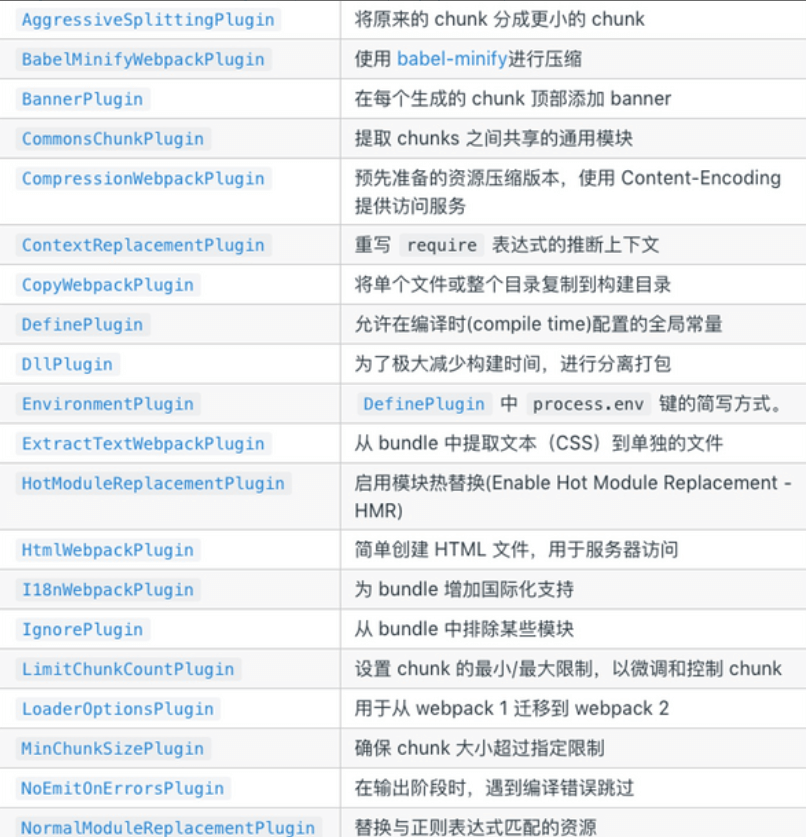
三、常见的Plugin
常见的plugin有如图所示:
下面介绍几个常用的插件用法:
HtmlWebpackPlugin
在打包结束后,⾃动生成⼀个 html ⽂文件,并把打包生成的 js 模块引⼊到该 html 中
1npm install --save-dev html-webpack-plugin
1// webpack.config.js 2const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require("html-webpack-plugin"); 3module.exports = { 4 ... 5 plugins: [ 6 new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ 7 title: "My App", 8 filename: "app.html", 9 template: "./src/html/index.html" 10 }) 11 ] 12};
1<!--./src/html/index.html--> 2<!DOCTYPE html> 3<html lang="en"> 4<head> 5 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 6 <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> 7 <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> 8 <title><%=htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title%></title> 9</head> 10<body> 11 <h1>html-webpack-plugin</h1> 12</body> 13</html>
在 html 模板中,可以通过 <%=htmlWebpackPlugin.options.XXX%> 的方式获取配置的值
更多的配置可以自寻查找
clean-webpack-plugin
删除(清理)构建目录
1npm install --save-dev clean-webpack-plugin
1const {CleanWebpackPlugin} = require('clean-webpack-plugin'); 2module.exports = { 3 ... 4 plugins: [ 5 ..., 6 new CleanWebpackPlugin(), 7 ... 8 ] 9}
mini-css-extract-plugin
提取 CSS 到一个单独的文件中
1npm install --save-dev mini-css-extract-plugin
1const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require('mini-css-extract-plugin');module.exports = { ..., module: { rules: [ { test: /\.s[ac]ss$/, use: [ { loader: MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader }, 'css-loader', 'sass-loader' ] } ] }, plugins: [ ..., new MiniCssExtractPlugin({ filename: '[name].css' }), ... ]}
DefinePlugin
允许在编译时创建配置的全局对象,是一个webpack内置的插件,不需要安装
1const { DefinePlugun } = require('webpack')module.exports = { ... plugins:[ new DefinePlugin({ BASE_URL:'"./"' }) ]}
这时候编译template模块的时候,就能通过下述形式获取全局对象
1<link rel="icon" href="<%= BASE_URL%>favicon.ico>"
copy-webpack-plugin
复制文件或目录到执行区域,如vue的打包过程中,如果我们将一些文件放到public的目录下,那么这个目录会被复制到dist文件夹中
1npm install copy-webpack-plugin -D
1new CopyWebpackPlugin({ parrerns:[ { from:"public", globOptions:{ ignore:[ '**/index.html' ] } } ]})
复制的规则在patterns属性中设置:
-
from:设置从哪一个源中开始复制
-
to:复制到的位置,可以省略,会默认复制到打包的目录下
-
globOptions:设置一些额外的选项,其中可以编写需要忽略的文件
最近更新时间:2024-01-25
赞赏支持

题库维护不易,您的支持就是我们最大的动力!
